Bahamas
Lucayan Indians inhabited the islands when Christopher COLUMBUS first set foot in the New World on San Salvador in 1492. British settlement of the islands began in 1647; the islands became a colony in 1783. Since attaining independence from the UK in 1973, The Bahamas has prospered through tourism, international banking, and investment management. Because of its location, the country is a major transshipment point for illegal drugs, particularly shipments to the US and Europe, and its territory is used for smuggling illegal migrants into the US.
Geography
Location:
chain of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean, southeast of Florida, northeast of Cuba
Geographic coordinates:
24 15 N, 76 00 W
Map references:
Central America and the Caribbean
Area:
total: 13,880 sq km
country comparison to the world: 161
land: 10,010 sq km
water: 3,870 sq km
Area – comparative:
slightly smaller than Connecticut
Land boundaries:
0 km
Coastline:
3,542 km
Maritime claims:
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
Climate:
tropical marine; moderated by warm waters of Gulf Stream
Terrain:
long, flat coral formations with some low rounded hills
Elevation extremes:
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
highest point: Mount Alvernia on Cat Island 63 m
Natural resources:
salt, aragonite, timber, arable land
Land use:
arable land: 0.65%
permanent crops: 0.29%
other: 99.06% (2011)
Irrigated land:
10 sq km (2003)
Total renewable water resources:
0.02 cu km (2011)
Natural hazards:
hurricanes and other tropical storms cause extensive flood and wind damage
Environment – current issues:
coral reef decay; solid waste disposal
Environment – international agreements:
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification,
Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Geography – note:
strategic location adjacent to US and Cuba; extensive island chain of which 30 are inhabited
People & Society
Nationality:
noun: Bahamian(s)
adjective: Bahamian
Ethnic groups:
black 90.6%, white 4.7%, black and white 2.1%, other 1.9%, unspecified 0.7% (2010 est.)
Languages:
English (official), Creole (among Haitian immigrants)
Religions:
Protestant 69.9% (includes Baptist 34.9%, Anglican 13.7%, Pentecostal 8.9% Seventh Day Adventist 4.4%, Methodist 3.6%, Church of God 1.9%, Brethren 1.6%), Roman Catholic 12%, other Christian 13% (includes Jehovah’s Witness 1.1%), other 0.6%, none 1.9%, unspecified 2.6% (2010 est.)
Population:
321,834
country comparison to the world: 179
note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected (July 2014 est.)
Age structure:
0-14 years: 23.2% (male 37,962/female 36,857)
15-24 years: 17.4% (male 28,387/female 27,639)
25-54 years: 44.1% (male 70,765/female 71,038)
55-64 years: 7% (male 11,882/female 14,885)
65 years and over: 6.7% (male 8,591/female 13,828) (2014 est.)
Dependency ratios:
total dependency ratio: 40.9 %
youth dependency ratio: 29.6 %
elderly dependency ratio: 11.3 %
potential support ratio: 8.9 (2014 est.)
Median age:
total: 31.2 years
male: 30.1 years
female: 32.3 years (2014 est.)
Population growth rate:
0.87% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 128
Birth rate:
15.65 births/1,000 population (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 126
Death rate:
7 deaths/1,000 population (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 133
Net migration rate:
0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 97
Urbanization:
urban population: 84.3% of total population (2011)
rate of urbanization: 1.37% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
Major urban areas – population:
NASSAU (capital) 254,000 (2011)
Sex ratio:
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.03 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.03 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.96 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.62 male(s)/female
total population: 0.96 male(s)/female (2014 est.)
Maternal mortality rate:
47 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)
country comparison to the world: 111
Infant mortality rate:
total: 12.5 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 124
male: 12.51 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 12.49 deaths/1,000 live births (2014 est.)
Life expectancy at birth:
total population: 71.93 years
country comparison to the world: 140
male: 69.48 years
female: 74.46 years (2014 est.)
Total fertility rate:
1.97 children born/woman (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 130
Health expenditures:
7.7% of GDP (2011)
country comparison to the world: 67
Physicians density:
2.82 physicians/1,000 population (2008)
Hospital bed density:
3.1 beds/1,000 population (2010)
Drinking water source:
improved:
urban: 96% of population
rural: 96% of population
total: 96% of population
unimproved:
urban: 4% of population
rural: 4% of population
total: 4% of population (2011 est.)
Sanitation facility access:
improved:
urban: 100% of population
rural: 100% of population
total: 100% of population (2010 est.)
HIV/AIDS – adult prevalence rate:
3.3% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 18
HIV/AIDS – people living with HIV/AIDS:
7,000 (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 117
HIV/AIDS – deaths:
300 (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 105
Obesity – adult prevalence rate:
34.7% (2008)
country comparison to the world: 13
Education expenditures:
NA
Literacy:
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 95.6%
male: 94.7%
female: 96.5% (2003 est.)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:
total: 30.8%
country comparison to the world: 25
male: 29.6%
female: 32.2% (2012)
Government
Country name:
conventional long form: Commonwealth of The Bahamas
conventional short form: The Bahamas
Government type:
constitutional parliamentary democracy and a Commonwealth realm
Capital:
name: Nassau
geographic coordinates: 25 05 N, 77 21 W
time difference: UTC-5 (same time as Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
daylight saving time: +1hr, begins second Sunday in March; ends first Sunday in November
Administrative divisions:
31 districts; Acklins Islands, Berry Islands, Bimini, Black Point, Cat Island, Central Abaco, Central Andros, Central Eleuthera, City of Freeport, Crooked Island and Long Cay, East Grand Bahama, Exuma, Grand Cay, Harbour Island, Hope Town, Inagua, Long Island, Mangrove Cay, Mayaguana, Moore’s Island, North Abaco, North Andros, North Eleuthera, Ragged Island, Rum Cay, San Salvador, South Abaco, South Andros, South Eleuthera, Spanish Wells, West Grand Bahama
Independence:
10 July 1973 (from the UK)
National holiday:
Independence Day, 10 July (1973)
Constitution:
previous 1964 (preindependence); latest adopted 20 June 1973, effective 10 July 1973; amended many times, last in 2002; note – in 2012, a constitutional commission was appointed to review and recommend constitutional changes (2013)
Legal system:
common law system based on the English model
International law organization participation:
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
Suffrage:
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch:
chief of state: Queen ELIZABETH II (since 6 February 1952); represented by Governor General Sir Arthur A. FOULKES (since 14 April 2010)
head of government: Prime Minister Perry CHRISTIE (since 8 May 2012)
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the governor general on the prime minister’s recommendation
(For more information visit the World Leaders website Opens in New Window)
elections: the monarchy is hereditary; governor general appointed by the monarch; following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or the leader of the majority coalition is usually appointed prime minister by the governor general; the prime minister recommends the deputy prime minister
Legislative branch:
bicameral Parliament consists of the Senate (16 seats; members appointed by the governor general upon the advice of the prime minister and the opposition leader to serve five-year terms) and the House of Assembly (38 seats; members elected by direct popular vote to serve five-year terms); the government may dissolve the parliament and call elections at any time
elections: last held on 7 May 2012 (next to be held by May 2017)
election results: percent of vote by party – NA; seats by party – PLP 30, FNM 8
Judicial branch:
highest court(s): The Bahamas Court of Appeal (consists of the court president and 4 justices, sitting in panels of 3 justices)
note – as of 2008, the Bahamas was not a party to the agreement establishing the Caribbean Court of Justice as the highest appellate court for the 15-member Caribbean Community (CARICOM); the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council (in London) serves as the final court of appeal for the Bahamas
judge selection and term of office: Court of Appeal justices appointed by the governor-general on the advice of the prime minister and in consultation with the Judicial and Legal
Services Commission; justices appointed for life with mandatory retirement at age 68-70
subordinate courts: Supreme Court; Industrial Tribunal; Stipendiary and Magistrates Courts; Family Island Administrators
Political parties and leaders:
Free National Movement or FNM [Hubert MINNIS]
Progressive Liberal Party or PLP [Perry CHRISTIE]
Political pressure groups and leaders:
Friends of the Environment
other: trade unions
International organization participation:
ACP, AOSIS, C, Caricom, CDB, CELAC, FAO, G-77, IADB, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, ITSO, ITU, LAES, MIGA, NAM, OAS, OPANAL, OPCW, Petrocaribe, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO (observer)
Diplomatic representation in the US:
chief of mission: Ambassador Dr. Eugene Glenwood NEWRY (since 3 December 2013)
chancery: 2220 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 319-2660
FAX: [1] (202) 319-2668
consulate(s) general: Atlanta, Miami, New York
Diplomatic representation from the US:
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d’ Affaires John DINKELMAN (since November 2011)
embassy: 42 Queen Street, Nassau, New Providence
mailing address: local or express mail address: P. O. Box N-8197, Nassau; US Department of State, 3370 Nassau Place, Washington, DC 20521-3370
telephone: [1] (242) 322-1181, 328-2206 (after hours)
FAX: [1] (242) 328-2206
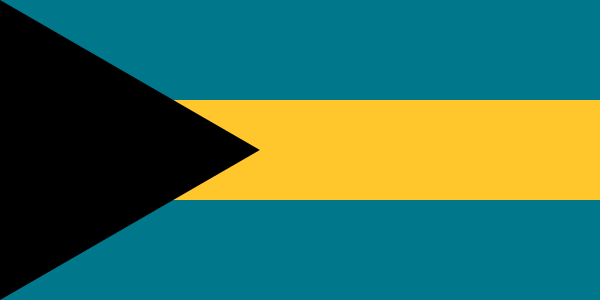
Flag description:
three equal horizontal bands of aquamarine (top), gold, and aquamarine, with a black equilateral triangle based on the hoist side; the band colors represent the golden beaches of the islands surrounded by the aquamarine sea; black represents the vigor and force of a united people, while the pointing triangle indicates the enterprise and determination of the Bahamian people to develop the rich resources of land and sea
National symbol(s):
blue marlin; flamingo
National anthem:
name: “March On, Bahamaland!”
Economy
Economy – overview:
The Bahamas is one of the wealthiest Caribbean countries with an economy heavily dependent on tourism and offshore banking. Tourism together with tourism-driven construction and manufacturing accounts for approximately 60% of GDP and directly or indirectly employs half of the archipelago’s labor force.
Financial services constitute the second-most important sector of the Bahamian economy and, when combined with business services, account for about 35% of GDP. Manufacturing and agriculture combined contribute less than a 10th of GDP and show little growth, despite government incentives aimed at those sectors.
The economy of The Bahamas shrank at an average pace of 0.8% annually between 2007-2011, and tourism, financial services, and construction – pillars of the national economy – remain subdued. Conditions are improving in the tourism sector, however, due to steady foreign investment led activity. New resort and marina developments are likely to provide sustained employment opportunities.
GDP (purchasing power parity):
$11.4 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 152
$11.19 billion (2012 est.)
$10.98 billion (2011 est.)
note: data are in 2013 US dollars
GDP (official exchange rate):
$8.373 billion (2013 est.)
GDP – real growth rate:
1.9% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 147
1.8% (` est.)
1.7% (2011 est.)
GDP – per capita (PPP):
$32,000 (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 43
$31,800 (2012 est.)
$31,500 (2011 est.)
note: data are in 2013 US dollars
Gross national saving:
14.3% of GDP (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 110
19.3% of GDP (2012 est.)
17.8% of GDP (2011 est.)
GDP – composition, by end use:
household consumption: 68.7%
government consumption: 15.5%
investment in fixed capital: 34.4%
investment in inventories: 0%
exports of goods and services: 45.8%
imports of goods and services: -64.4%
(2013 est.)
GDP – composition, by sector of origin:
agriculture: 2.1%
industry: 7.1%
services: 90.8% (2013 est.)
Agriculture – products:
citrus, vegetables; poultry
Industries:
tourism, banking, oil bunkering, maritime industries, transshipment, salt, rum, aragonite, pharmaceuticals
Industrial production growth rate:
1.5%
country comparison to the world: 133
Labor force:
196,900 (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 171
Labor force – by occupation:
agriculture: 3%
industry: 11%
tourism: 49%
other services: 37% (2011 est.)
Unemployment rate:
16.2% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 145
14% (2012 est.)
Population below poverty line:
9.3% (2010 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
lowest 10%: 1%
highest 10%: 22% (2007)
Budget:
revenues: $1.41 billion
expenditures: $2.1 billion (2012 est.)
Taxes and other revenues:
16.8% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 183
Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):
-8.2% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 197
Fiscal year:
1 July – 30 June
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
1% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 26
2% (2012 est.)
Central bank discount rate:
4.5% (1 January 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 80
4.5% (31 December 2012 est.)
Commercial bank prime lending rate:
4.75% (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 154
4.75% (31 December 2012 est.)
Stock of narrow money:
$1.435 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 139
$1.575 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
Stock of broad money:
$6.329 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 121
$6.088 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
Stock of domestic credit:
$9.2 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 99
$8.653 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
Market value of publicly traded shares:
$NA (31 December 2012 est.)
Current account balance:
-$1.372 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 129
-$1.424 billion (2012 est.)
Exports:
$960 million (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 162
$984 million (2012 est.)
Exports – commodities:
crawfish, aragonite, crude salt, polystyrene products
Exports – partners:
Singapore 25.1%, US 20.6%, Dominican Republic 12.9%, Ecuador 9.4%, Canada 5.8%, Switzerland 4.1%, China 4.1% (2012)
Imports:
$3.245 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 144
$3.386 billion (2012 est.)
Imports – commodities:
machinery and transport equipment, manufactures, chemicals, mineral fuels; food and live animals
Imports – partners:
US 30.1%, India 20.3%, Singapore 8.7%, South Korea 6.8%, China 5%, Colombia 4.5%, Canada 4.2% (2012)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:
$830 million (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 142
$846.9 million (31 December 2012 est.)
Debt – external:
$17.56 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 85
$16.35 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
Exchange rates:
Bahamian dollars (BSD) per US dollar –
1 (2013 est.)
1 (2012 est.)
1 (2010 est.)
1 (2008 est.)
1 (2007 est.)