Denmark
Once the seat of Viking raiders and later a major north European power, Denmark has evolved into a modern, prosperous nation that is participating in the general political and economic integration of Europe. It joined NATO in 1949 and the EEC (now the EU) in 1973. However, the country has opted out of certain elements of the European Union’s Maastricht Treaty, including the European Economic and Monetary Union (EMU), European defense cooperation, and issues concerning certain justice and home affairs.
Geography
Location:
Northern Europe, bordering the Baltic Sea and the North Sea, on a peninsula north of Germany (Jutland); also includes several major islands (Sjaelland, Fyn, and Bornholm)
Geographic coordinates:
56 00 N, 10 00 E
Map references:
Europe
Area:
total: 43,094 sq km
country comparison to the world: 134
land: 42,434 sq km
water: 660 sq km
note: includes the island of Bornholm in the Baltic Sea and the rest of metropolitan Denmark (the Jutland Peninsula, and the major islands of Sjaelland and Fyn), but excludes the Faroe Islands and Greenland
Area – comparative:
slightly less than twice the size of Massachusetts
Land boundaries:
total: 68 km
border countries: Germany 68 km
Coastline:
7,314 km
Maritime claims:
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200 m depth or to the depth of exploitation
Climate:
temperate; humid and overcast; mild, windy winters and cool summers
Terrain:
low and flat to gently rolling plains
Elevation extremes:
lowest point: Lammefjord -7 m
highest point: Mollehoj/Ejer Bavnehoj 171 m
Natural resources:
petroleum, natural gas, fish, salt, limestone, chalk, stone, gravel and sand
Land use:
arable land: 57.99%
permanent crops: 0.09%
other: 41.91% (2011)
Irrigated land:
4,354 sq km (2007)
Total renewable water resources:
6 cu km (2011)
Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):
total: 0.66 cu km/yr (58%/5%/36%)
per capita: 118.4 cu m/yr (2009)
Natural hazards:
flooding is a threat in some areas of the country (e.g., parts of Jutland, along the southern coast of the island of Lolland) that are protected from the sea by a system of dikes
Environment – current issues:
air pollution, principally from vehicle and power plant emissions; nitrogen and phosphorus pollution of the North Sea; drinking and surface water becoming polluted from animal wastes and pesticides
Environment – international agreements:
party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Geography – note:
controls Danish Straits (Skagerrak and Kattegat) linking Baltic and North Seas; about one-quarter of the population lives in greater Copenhagen
People & Society
Nationality:
noun: Dane(s)
adjective: Danish
Ethnic groups:
Scandinavian, Inuit, Faroese, German, Turkish, Iranian, Somali
Languages:
Danish, Faroese, Greenlandic (an Inuit dialect), German (small minority)
note: English is the predominant second language
Religions:
Evangelical Lutheran (official) 80%, Muslim 4%, other (denominations of less than 1% each, includes Roman Catholic, Jehovah’s Witness, Serbian Orthodox Christian, Jewish, Baptist, and Buddhist) 16% (2012 est.)
Population:
5,569,077 (July 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 115
Age structure:
0-14 years: 17% (male 485,115/female 460,682)
15-24 years: 13.1% (male 371,258/female 355,984)
25-54 years: 39.2% (male 1,087,993/female 1,093,545)
55-64 years: 18.4% (male 343,685/female 347,732)
65 years and over: 18% (male 457,175/female 565,908) (2014 est.)
Dependency ratios:
total dependency ratio: 55.6 %
youth dependency ratio: 27.1 %
elderly dependency ratio: 28.5 %
potential support ratio: 3.5 (2014 est.)
Median age:
total: 41.6 years
male: 40.7 years
female: 42.5 years (2014 est.)
Population growth rate:
0.22% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 178
Birth rate:
10.22 births/1,000 population (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 190
Death rate:
10.23 deaths/1,000 population (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 46
Net migration rate:
2.25 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 43
Urbanization:
urban population: 86.9% of total population (2011)
rate of urbanization: 0.5% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
Major urban areas – population:
COPENHAGEN (capital) 1.206 million (2011)
Sex ratio:
at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.97 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.8 male(s)/female
total population: 0.97 male(s)/female (2014 est.)
Mother’s mean age at first birth:
29.1 (2012 est.)
Maternal mortality rate:
12 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)
country comparison to the world: 151
Infant mortality rate:
total: 4.1 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 197
male: 4.17 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 4.02 deaths/1,000 live births (2014 est.)
Life expectancy at birth:
total population: 79.09 years
country comparison to the world: 47
male: 76.68 years
female: 81.64 years (2014 est.)
Total fertility rate:
1.73 children born/woman (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 168
Health expenditures:
11.2% of GDP (2011)
country comparison to the world: 12
Physicians density:
3.42 physicians/1,000 population (2007)
Hospital bed density:
3.5 beds/1,000 population (2010)
Drinking water source:
improved:
urban: 100% of population
rural: 100% of population
total: 100% of population
unimproved:
urban: 0% of population
rural: 0% of population
total: 0% of population (2011 est.)
Sanitation facility access:
improved:
urban: 100% of population
rural: 100% of population
total: 100% of population
unimproved:
urban: 0% of population
rural: 0% of population
total: 0% of population (2011 est.)
HIV/AIDS – adult prevalence rate:
0.2% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 111
HIV/AIDS – people living with HIV/AIDS:
5,300 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 122
HIV/AIDS – deaths:
fewer than 100 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 133
Obesity – adult prevalence rate:
18.2% (2008)
country comparison to the world: 107
Education expenditures:
8.7% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 8
Literacy:
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 99%
male: 99%
female: 99% (2003 est.)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):
total: 17 years
male: 16 years
female: 18 years (2010)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:
total: 14.2%
country comparison to the world: 89
male: 14.8%
female: 14.1% (2012)
Government
Country name:
conventional long form: Kingdom of Denmark
conventional short form: Denmark
local long form: Kongeriget Danmark
local short form: Danmark
Government type:
constitutional monarchy
Capital:
name: Copenhagen
geographic coordinates: 55 40 N, 12 35 E
time difference: UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
note: applies to continental Denmark only, not to its North Atlantic components
Administrative divisions:
metropolitan Denmark – 5 regions (regioner, singular – region); Hovedstaden (Capital), Midtjylland (Central Jutland), Nordjylland (North Jutland), Sjaelland (Zealand), Syddanmark (Southern Denmark)
note: an extensive local government reform merged 271 municipalities into 98 and 13 counties into five regions, effective 1 January 2007
Independence:
ca. 965 (unified and Christianized under HARALD I Gormson); 5 June 1849 (became a constitutional monarchy)
National holiday:
none designated; Constitution Day, 5 June (1849) is generally viewed as the National Day
Constitution:
previous 1665; latest adopted 5 June 1849; amended several times, last in 2009 (2009)
Legal system:
civil law; judicial review of legislative acts
International law organization participation:
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
Suffrage:
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch:
chief of state: Queen MARGRETHE II (since 14 January 1972); Heir Apparent Crown Prince FREDERIK, elder son of the monarch (born on 26 May 1968)
head of government: Prime Minister Helle THORNING-SCHMIDT (since 3 October 2011)
cabinet: Council of State appointed by the monarch
(For more information visit the World Leaders website Opens in New Window)
elections: the monarchy is hereditary; following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or the leader of the majority coalition usually appointed prime minister by the monarch
Legislative branch:
unicameral People’s Assembly or Folketing (179 seats, including 2 from Greenland and 2 from the Faroe Islands; members elected by popular vote on the basis of proportional representation to serve four-year terms unless the Folketing is dissolved earlier)
elections: last held on 15 September 2011 (next to be held by September 2015)
election results: percent of vote by party – V 26.7%, SDP 24.9%, DF 12.3%, SLP 9.5%, SF 9.2%, O 6.7%, LA 5%, C 4.9%, other 0.8%; seats by party – V 47, SDP 44, DF 22, SLP 17, SF 16, O 12, LA 9, C 8; note – does not include the two seats from Greenland and the two seats from the Faroe Islands
Judicial branch:
highest court(s): Supreme Court (consists of the court president and 18 judges)
judge selection and term of office: judges appointed by the monarch upon the recommendation of the Minister of Justice with the advice of the Judicial Appointments Council, a 6-member independent body of judges and lawyers; judges appointed for life with retirement at age 70
subordinate courts: Special Court of Indictment and Revision; 2 High Courts; Maritime and Commercial Court; county courts
Political parties and leaders:
Conservative People’s Party or C [Lars BARFOED]
Danish People’s Party or DF [Kristian THULESEN DAHL]
Liberal Alliance or LA [Anders SAMUELSEN]
Liberal Party or V [Lars LOKKE RAMUSSEN]
Red-Green Alliance (Unity List) or O [collective leadership, spokesperson Johanne SCHMIDT-NIELSEN]
Social Democratic Party or SDP [Helle THORNING-SCHMIDT]
Social Liberal Party or SLP [Margrethe VESTAGER]
Socialist People’s Party or SF [Annette VILHELMSEN]
Political pressure groups and leaders:
Confederation of Danish Employers or DA [President Jorn Neergaard LARSEN]
Confederation of Danish Industries [CEO Karsten DYBVAD]
Confederation of Danish Labor Unions (Landsorganisationen) or LO [President Harald BORSTING]
Danish Shipowners’ Association [Chairman Carsten MORTENSEN]; Danish Bankers Association [CEO Joergen HORWITZ]
DaneAge Association [President Bjarne HASTRUP]
Danish Society for Nature Conservation [President Ella Maria BISSCHOP-LARSEN]
other: environmental groups; humanitarian relief; development assistance; human rights NGOs
International organization participation:
ADB (nonregional member), AfDB (nonregional member), Arctic Council, Australia Group, BIS, CBSS, CD, CE, CERN, EAPC, EBRD, EIB, EITI (implementing country), ESA, EU, FAO, FATF, G-9, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IGAD (partners), IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MINUSMA, NATO, NC, NEA, NIB, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OPCW, OSCE, Paris Club, PCA, Schengen Convention, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNRWA, UNTSO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
Diplomatic representation in the US:
chief of mission: Ambassador Peter TAKSOE-JENSEN (since 1 September 2010)
chancery: 3200 Whitehaven Street NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 234-4300
FAX: [1] (202) 328-1470
consulate(s) general: Chicago, New York
Diplomatic representation from the US:
chief of mission: Ambassador Rufus GIFFORD (since 15 August 2013)
embassy: Dag Hammarskjolds Alle 24, 2100 Copenhagen 0
mailing address: Unit 5280, DPO, AE 09716
telephone: [45] 33 41 71 00
FAX: [45] 35 43 02 23
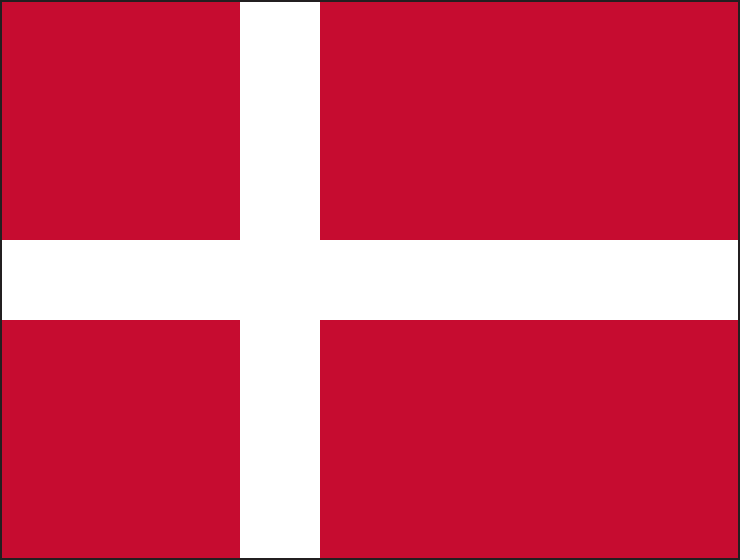
Flag description:
red with a white cross that extends to the edges of the flag; the vertical part of the cross is shifted to the hoist side; the banner is referred to as the Dannebrog (Danish flag) and is one of the oldest national flags in the world; traditions as to the origin of the flag design vary, but the best known is a legend that the banner fell from the sky during an early-13th century battle; caught up by the Danish king before it ever touched the earth, this heavenly talisman inspired the royal army to victory; in actuality, the flag may derive from a crusade banner or ensign
note: the shifted design element was subsequently adopted by the other Nordic countries of Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden
National symbol(s):
lion; mute swan
National anthem:
name: “Der er et yndigt land” (There is a Lovely Land); “Kong Christian” (King Christian)
Economy
Economy – overview:
This thoroughly modern market economy features a high-tech agricultural sector, state-of-the-art industry with world-leading firms in pharmaceuticals, maritime shipping and renewable energy, and a high dependence on foreign trade. Denmark is a member of the European Union (EU); Danish legislation and regulations conform to EU standards on almost all issues. Danes enjoy a high standard of living and the Danish economy is characterized by extensive government welfare measures and an equitable distribution of income.
Denmark is a net exporter of food and energy and enjoys a comfortable balance of payments surplus, but depends on imports of raw materials for the manufacturing sector. Within the EU, Denmark is among the strongest supporters of trade liberalization. After a long consumption-driven upswing, Denmark’s economy began slowing in 2007 with the end of a housing boom. Housing prices dropped markedly in 2008-09 and, following a short respite in 2010, have since continued to decline. Household indebtedness is still relatively high at more than 275% of gross disposable income in the first half of 2013. The global financial crisis has exacerbated this cyclical slowdown through increased borrowing costs and lower export demand, consumer confidence, and investment. Denmark made a modest recovery in 2010, in part because of increased government spending; however, the country experienced a technical recession in late 2010-early 2011.
Historically low levels of unemployment rose sharply with the recession and have remained at about 6% in 2010-13, based on the national measure, about two-thirds average EU unemployment. An impending decline in the ratio of workers to retirees will be a major long-term issue. Denmark maintained a healthy budget surplus for many years up to 2008, but the budget balance swung into deficit in 2009, where it remains. In spite of the deficits, the new coalition government delivered a modest stimulus to the economy in 2012. Nonetheless, Denmark’s fiscal position remains among the strongest in the EU with public debt at about 46% of GDP in 2013. Despite previously meeting the criteria to join the European Economic and Monetary Union (EMU), so far Denmark has decided not to join, although the Danish krone remains pegged to the euro.
GDP (purchasing power parity):
$211.3 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 55
$211.1 billion (2012 est.)
$211.9 billion (2011 est.)
note: data are in 2013 US dollars
GDP (official exchange rate):
$324.3 billion (2013 est.)
GDP – real growth rate:
0.1% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 194
-0.4% (2012 est.)
1.1% (2011 est.)
GDP – per capita (PPP):
$37,800 (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 32
$37,800 (2012 est.)
$38,100 (2011 est.)
note: data are in 2013 US dollars
Gross national saving:
24.1% of GDP (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 55
NA% (2012 est.)
NA% (2011 est.)
GDP – composition, by end use:
household consumption: 49.1%
government consumption: 28.8%
investment in fixed capital: 17.7%
investment in inventories: 0.2%
exports of goods and services: 53.4%
imports of goods and services: -49.2%
(2013 est.)
GDP – composition, by sector of origin:
agriculture: 1.5%
industry: 21.7%
services: 76.8% (2013 est.)
Agriculture – products:
barley, wheat, potatoes, sugar beets; pork, dairy products; fish
Industries:
iron, steel, nonferrous metals, chemicals, food processing, machinery and transportation equipment, textiles and clothing, electronics, construction, furniture and other wood products, shipbuilding and refurbishment, windmills, pharmaceuticals, medical equipment
Industrial production growth rate:
1.1% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 143
Labor force:
2.795 million (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 106
Labor force – by occupation:
agriculture: 2.6%
industry: 20.3%
services: 77.1% (2011 est.)
Unemployment rate:
6% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 59
6% (2012 est.)
Population below poverty line:
13.4% (2011)
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
lowest 10%: 1.9%
highest 10%: 28.7% (2007)
Distribution of family income – Gini index:
24.8 (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 137
24.7 (1992)
Budget:
revenues: $181.4 billion
expenditures: $189.7 billion (2013 est.)
Taxes and other revenues:
55.9% of GDP (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8
Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):
-2.5% of GDP (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 103
Public debt:
47% of GDP (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 75
45.6% of GDP (2012 est.)
note: data cover general government debt, and includes debt instruments issued (or owned) by government entities other than the treasury; the data include treasury debt held by foreign entities; the data include debt issued by subnational entities, as well as intra-governmental debt; intra-governmental debt consists of treasury borrowings from surpluses in the social funds, such as for retirement, medical care, and unemployment; debt instruments for the social funds are not sold at public auctions
Fiscal year:
calendar year
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
0.8% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 18
2.4% (2012 est.)
Central bank discount rate:
0.75% (31 December 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 133
0.75% (31 December 2010 est.)
Commercial bank prime lending rate:
3.6% (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 162
3.6% (31 December 2012 est.)
Stock of narrow money:
$147.6 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 26
$150.4 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
Stock of broad money:
$180.2 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 42
$174.3 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
Stock of domestic credit:
$675 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
$664.5 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
Market value of publicly traded shares:
$NA (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 31
$179.5 billion (31 December 2011)
$231.7 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
Current account balance:
$19.6 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 16
$17.44 billion (2012 est.)
Exports:
$106 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 37
$104.9 billion (2012 est.)
Exports – commodities:
machinery and instruments, meat and meat products, dairy products, fish, pharmaceuticals, furniture, windmills
Exports – partners:
Germany 15.9%, Sweden 13.5%, UK 9.6%, US 6.6%, Norway 6.3%, Netherlands 4.6% (2012)
Imports:
$98.45 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 35
$96.77 billion (2012 est.)
Imports – commodities:
machinery and equipment, raw materials and semimanufactures for industry, chemicals, grain and foodstuffs, consumer goods
Imports – partners:
Germany 21.2%, Sweden 13.5%, Netherlands 7.5%, China 6.4%, Norway 6.3%, UK 5.6% (2012)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:
$89.5 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 24
$89.7 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
Debt – external:
$586.7 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 24
$571.4 billion (31 December 2011)
Stock of direct foreign investment – at home:
$146 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 31
$147.1 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
Stock of direct foreign investment – abroad:
$248.3 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
$241.7 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
Exchange rates:
Danish kroner (DKK) per US dollar –
5.695 (2013 est.)
5.7925 (2012 est.)
5.6241 (2010 est.)
5.361 (2009)
5.0236 (2008)